Summary ch.1 part 1 chemistry 3rd secondary
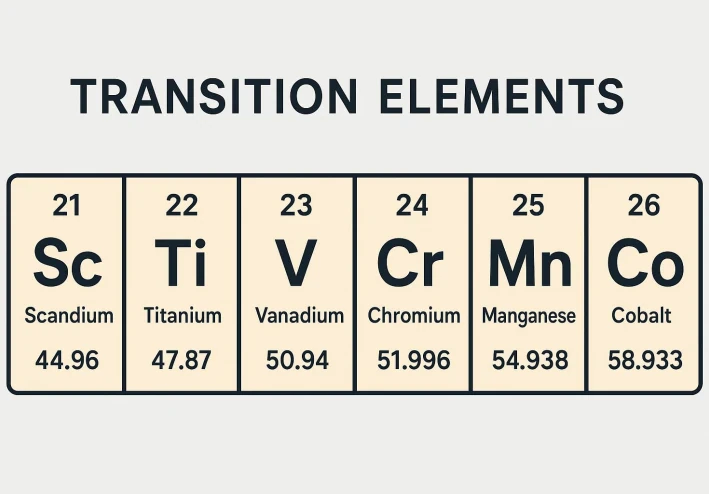
Transition Elements
Transition elements are:
Main Transition (d-block): These elements are found in the d-block of the periodic table.
Inner Transition (f-block): These elements are found in the f-block of the periodic table, which includes the lanthanides and actinides.
الأرقام اللاتينية:
I = 1
II = 2
III = 3
IV = 4
V = 5
VI = 6
VII = 7
VIII = 8
---
d-block (Transition Elements)
Location: Found in the middle section of the periodic table.
Divided into four series:
1. First Transition Series (3d series): Scandium (Sc21) to Zinc (Zn30), located in the 4th period.
2. Second Transition Series (4d series): Yttrium (Y39) to Cadmium (Cd48), located in the 5th period.
3. Third Transition Series (5d series): Lanthanum (La57) to Mercury (Hg80), located in the 6th period.
4. Fourth Transition Series (6d series).
Note: عمود رقم (8,9,10) كلهم جروب واحد اسمه (group 8).
---
Elements in First Transition Series
أعلى نسبة وجود Fe.
أقل نسبة وجود Sc.
Applications of Scandium:
1. Scandium-Aluminum Alloy: Described as "light and very hard," used in “Mig fighter jets.”
2. Scandium in Mercury Vapor Lamps: Used "to produce strong light like sunlight," making it suitable for “TV photography at night.”
---
2) Titanium (Ti22)
Properties: Strong like steel but with lower density.
Applications:
1. Titanium-Aluminum alloys are used in the manufacture of aircraft and space shuttles because they maintain their durability at high temperatures.
2. Dental Implants and Artificial Joints: Used in these applications because titanium is an inert element, meaning the body does not readily reject it, and it is non-poisonous.
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2):
Applications: Sun Protection Cosmetics: Used in sunscreens and other cosmetics because its nanoparticles prevent the effect of ultraviolet (UV) rays on the skin, acting as a physical barrier to reflect and scatter UV radiation.
---
3) Uses of Vanadium
1. Vanadium (Ferrovanadium Alloy with Steel): Used in car springs because adding a small amount of Vanadium to the steel gives hardness and ability to resist corrosion (rust).
2. Vanadium Pentoxide (V2O5):
Used in dyes for glass and ceramics.
Used as a catalyst in the manufacture of strong magnetic conductors.
---
4) Summary of the Notes on Chromium
Uses of Chromium:
1. Leather Tanning.
2. Metal Painting (plating): Chromium is used in metal plating and painting due to its chemical activity and resistance to atmospheric air, due to “passivity.”
Passivity:
Definition: Formation of a non-porous layer of metal oxide which prevents further oxidation, corrosion, and rust of the underlying metal.
Compounds of Chromium:
1. Chromium (III) Oxide (Cr₂O₃): Used in dyes.
2. Potassium Dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇): Used as an oxidizing agent
---
5) Manganese (Mn) (الهش)
Properties:
Manganese is a brittle metal and is not used in its pure form in industries because of this property.
Instead, it is predominantly used as an alloy or a component within compounds.
Uses of Manganese Alloys:
1. Ferro Manganese Alloy (Steel + Manganese): Used in railway tracks because the addition of manganese makes steel harder and stronger than steel.
2. Manganese with Aluminum Alloy: Used in soft drink cans due to its ability to resist corrosion.